Last modified: Jan 10, 2023 By Alexander Williams
Understand How to Use django HttpResponseNotFound
In this tutorial, we'll learn how to use Django HttpResponseNotFound and the difference between HttpResponseNotFound and HttpResponse.
1. What is HttpResponseNotFound
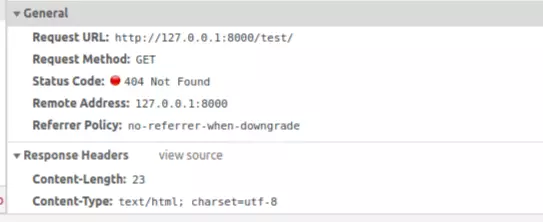
HttpResponseNotFound: is a class that returns a response with 404 status
2. Using HttpResponseNotFound with examples
let's create a simpe view that returns a "No page Found" response.
But, first we need to import HttpResponseNotFound.
fromdjango.httpimport HttpResponseNotFound
example #1:
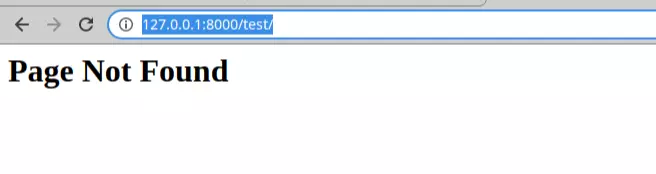
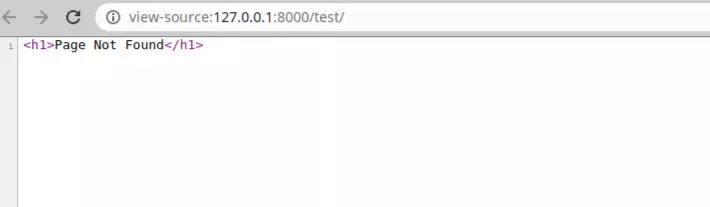
defresponse_not_found_ex(request): return HttpResponseNotFound("<h1>Page Not Found</h1>")
Result:
Page View Source:
Response Status:
3. Why HttpResponseNotFound?
For example, let's say we want to return a model Queryset, and if the Queryset is empty, the client we'll get 404 Response.
defresponse_not_found_ex(request): obj = Comments.objects.all() ifnot obj: return HttpResponseNotFound("<h1>Page Not Found</h1>")
this is just one of many things you can do with HttpResponseNotFound
4. Difference between HttpResponseNotFound and HttpResponse
HttpResponseNotFound: returns a response with 404 status.
HttpResponse: returns a response with 200 status by default.
To be sure, let's see these two examples.
example #1: with HttpResponseNotFound
defresponse_not_found_ex(request): return HttpResponseNotFound("<h1>Page Not Found</h1>")
Response's Status:

example #2: with HttpResponse
defresponse_not_found_ex(request): return HttpResponse("<h1>Page Not Found</h1>")
Response's Status: