Last modified: Jan 10, 2023 By Alexander Williams
How to build a currency converter in Django
This article will explain how to build a currency converter app. This app can convert from to all world currencies.
First of all, let's see what we'll build:
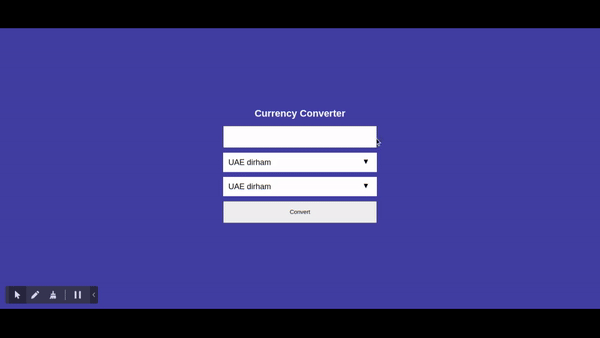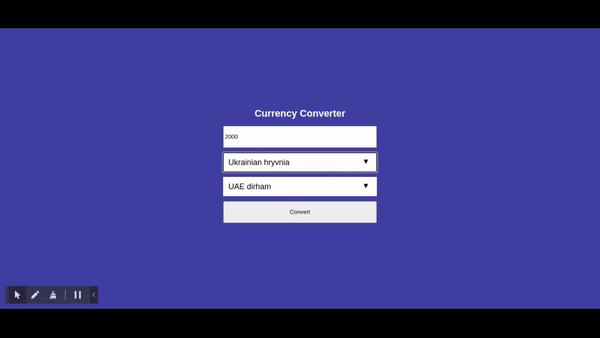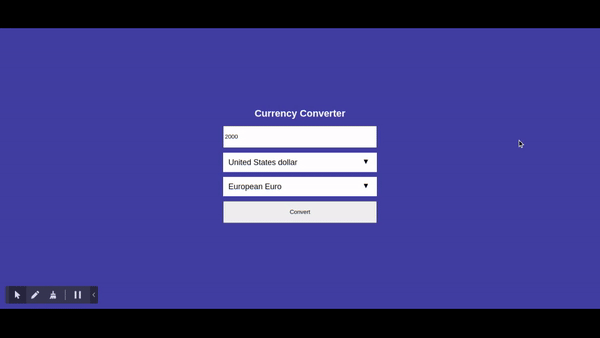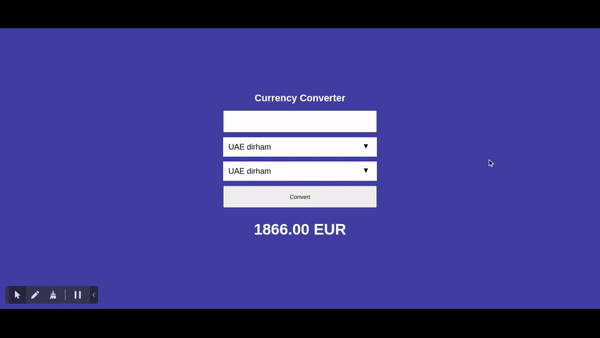
Now let's get started.
Technologies
In this tutorial, we'll use these requirements:
- Django==4.0.4
- requests==2.27.1
- open.er-api.com API
Project structure
After installing and creating the Django project, this is what the project structure looks like:
├── currency_converter
│ ├── core
│ │ ├── admin.py
│ │ ├── apps.py
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── migrations
│ │ ├── models.py
│ │ ├── __pycache__
│ │ ├── tests.py
│ │ └── views.py
│ ├── currency_converter
│ │ ├── asgi.py
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── __pycache__
│ │ ├── settings.py
│ │ ├── urls.py
│ │ └── wsgi.py
│ ├── db.sqlite3
│ ├── manage.py
│ └── TEMPLATES
│ └── index.html
Build a currency converter
To build a currency converter, we first need countries' currency data. Therefore we will download currencies.json from Github currencies data and put it in the core directory.
currencies.json:
[
{"cc":"AED","symbol":"\u062f.\u0625;","name":"UAE dirham"},
{"cc":"AFN","symbol":"Afs","name":"Afghan afghani"},
{"cc":"ALL","symbol":"L","name":"Albanian lek"},
{"cc":"AMD","symbol":"AMD","name":"Armenian dram"},
{"cc":"ANG","symbol":"NA\u0192","name":"Netherlands Antillean gulden"},
{"cc":"AOA","symbol":"Kz","name":"Angolan kwanza"},
{"cc":"ARS","symbol":"$","name":"Argentine peso"},
{"cc":"AUD","symbol":"$","name":"Australian dollar"},
{"cc":"AWG","symbol":"\u0192","name":"Aruban florin"},
{"cc":"AZN","symbol":"AZN","name":"Azerbaijani manat"},
..
..
.In view.py, we need to write a function that converts currencies.json to a dictionary.
from django.shortcuts import render
import requests
import json
import os
def currency_data():
""" All countries' currency data """
module_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__) # get current directory
file_path = os.path.join(module_dir, 'currencies.json')
with open(file_path, "r") as f:
currency_data = json.loads(f.read())
return currency_data
Next, create our converter page view and return the currency_data() function in it.
def index(request):
return render(request, "index.html", {"currency_data":currency_data()})Next, in the index.html, we'll write the converter form.
<html>
<head>
<title>Currency converter</title>
<style>
*, *:before, *:after {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
html, body {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
font: normal 10px 'Open Sans', sans-serif;
margin: 0;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
color: #4c4c4c;
background: #3f44a5;
}
.clear {
clear: both;
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
font-size: 22px;
color: white;
}
.select-wrapper {
position: relative;
width: 350px;
}
.select-wrapper::after {
color: black;
content: '▾';
margin-right: 10px;
pointer-events: none;
position: absolute;
right: 10px;
top: 7px;
font-size: 20px;
}
.select {
-moz-appearance: none;
-webkit-appearance: none;
background: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 0;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 12px;
width: 100%;
font-size: 18px;
}
.select:focus {
color: black;
}
.select::-ms-expand {
display: none;
}
input{ width: 100%; height: 50px;}
h2 {color: #fff; text-align: center; font-size: 35px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Currency Converter</h1>
<form method="post" action="{% url 'index' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
<!-- Amount input -->
<div class="select-text">
<input name="amount" type="text">
</div>
<br>
<div class="select-wrapper">
<!-- From options -->
<select name="currency_from" class="select">
{% for c in currency_data %}
<option value="{{c.cc}}">{{c.name}}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
</div>
<br>
<div class="select-wrapper">
<!-- To options -->
<select name="currency_to" class="select">
{% for c in currency_data %}
<option value="{{c.cc}}">{{c.name}}</option>
{% endfor %}
</select>
</div>
<br>
<div class="select-submit">
<input type="submit" value="Convert">
</div>
<!-- Converter result -->
<h2>{{ result }} {{ currency_to }}</h2>
</div>
</body>
</html>Next, in urls.py, we need to add a path for our index view.
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
# Views
from core.views import index
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
# Index
path('', index, name='index')
]
Now, let's see the result on the browser.
open http://127.0.0.1:8000/
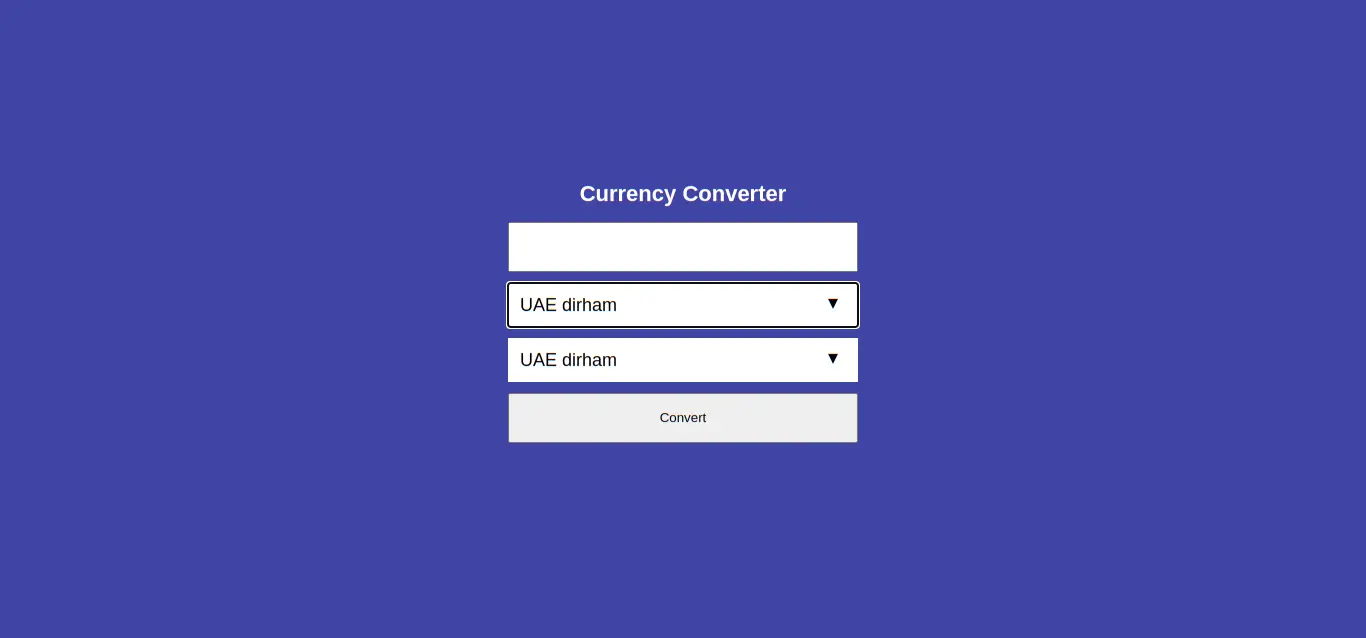
Now, it's time to write our form handling in view.py inside the index view.
def index(request):
if request.method == "POST":
# Get data from the html form
amount = float(request.POST.get('amount'))
currency_from = request.POST.get("currency_from")
currency_to = request.POST.get("currency_to")
# Get currency exchange rates
url = f"https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/{currency_from}"
d = requests.get(url).json()
# Converter
if d["result"] == "success":
# Get currency exchange of the target
ex_target = d["rates"][currency_to]
# Mltiply by the amount
result = ex_target * amount
# Set 2 decimal places
result = "{:.2f}".format(result)
context = {
"result":result,
"currency_to":currency_to,
"currency_data":currency_data()
}
return render(request, "index.html", context)
return render(request, "index.html", {"currency_data":currency_data()})To understand The logic to calculate the converter, let's say we want to convert 100 U.S dollars to Euro:
- Send a request to https://open.er-api.com/v6/latest/USD
- Get the exchange rate of the U.S dollar to Euro
- Multiply exchange rate of Euro by 100
Here is the final project:

You can also download the project via GitHub by clicking the following link:
Project on Github
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we've learned how to build the currency converter. To make the app stable, you need to add more form validations.
If you want to see how to build a translator app, check the link below:
Django Translator | Building a Translator app Step by Step
Happy Coding ♥